What Are Common Urine Crystals and Their Shapes? (Calcium Oxalate, Cysteine, Struvite, Uric Acid)
Published on 03/01/2025 · 4 min readHave you ever wondered what those tiny particles in urine sediment under a microscope could mean? Identifying urine crystals by their distinct shapes can provide valuable clues about the type of kidney stones a person might have. This is a high-yield topic, especially for medical board exams!
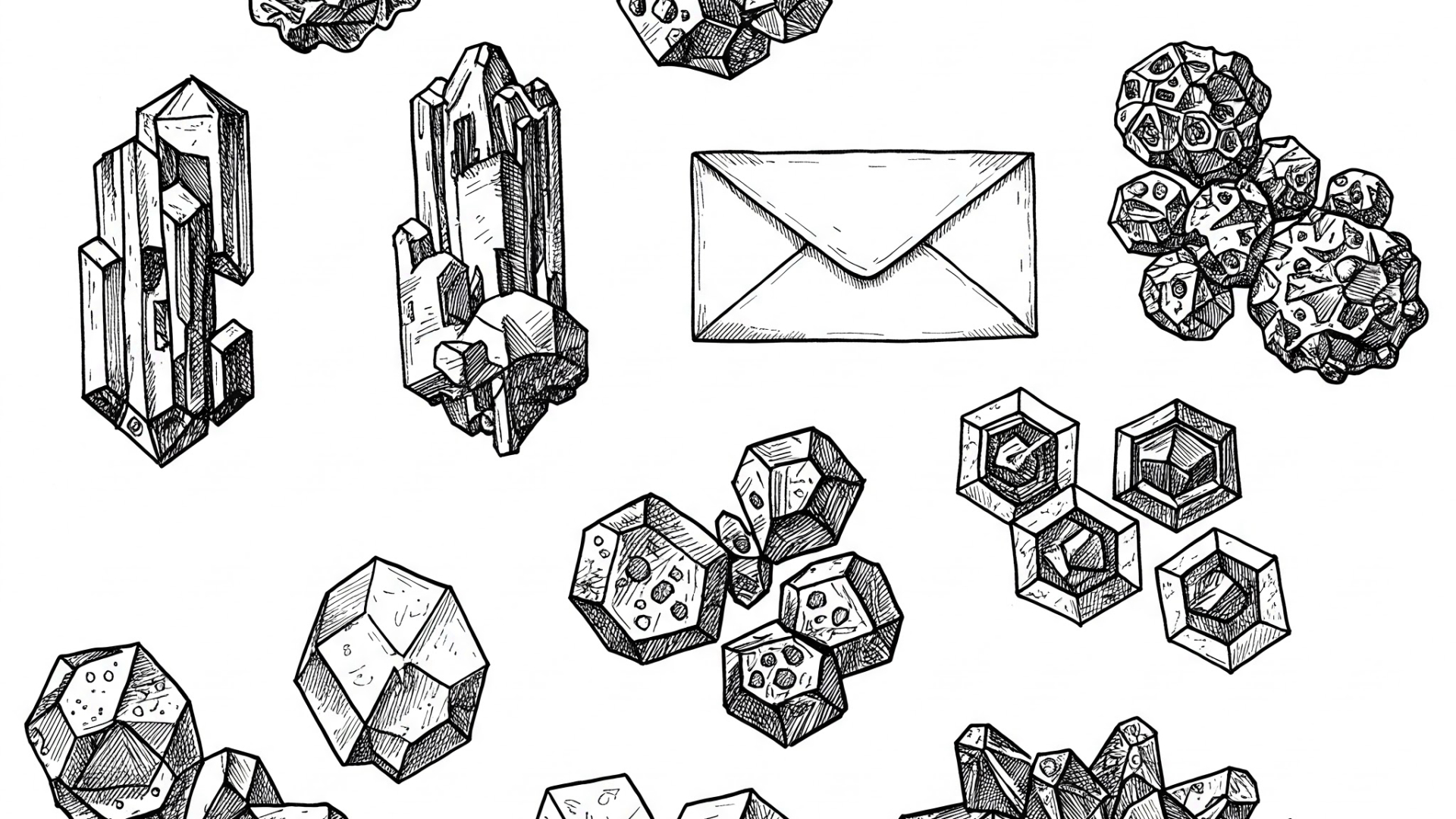
Table of Contents
Understanding Urine Crystals and Kidney StonesKey Urine Crystals and Their ShapesCalcium Oxalate: The Envelope ShapeCysteine: The Hexagonal FormStruvite: The Coffin Lid AppearanceUric Acid: The Rhomboid StructureWhy is Identifying Urine Crystal Shapes Important?
Understanding Urine Crystals and Kidney Stones
Urine crystals are formed when certain substances in urine become concentrated and solidify. Recognizing their morphology is key to understanding potential underlying conditions and the composition of kidney stones.
Key Urine Crystals and Their Shapes
Let's explore some of the most commonly encountered urine crystals:
Calcium Oxalate: The Envelope Shape
Calcium oxalate crystals are frequently seen and are characterized by their distinctive envelope shape. Fun fact: calcium oxalate stones are the most common type of kidney stones. Think of sending and receiving mail – envelopes are everywhere!
Cysteine: The Hexagonal Form
Cysteine crystals have a unique hexagonal shape. A simple way to remember this? The word "sis" sounds a bit like "six," which relates to the six sides of a hexagon. This association can help you recall the shape of cysteine crystals.
Struvite: The Coffin Lid Appearance
Struvite stones are often linked to infections and can be quite problematic. Their crystals exhibit a characteristic coffin shape. You might remember this by associating "struvite" with something negative, and a coffin is often linked to somber events.
Uric Acid: The Rhomboid Structure
Uric acid crystals typically appear as rhomboid shapes. These crystals are sometimes associated with conditions like gout, where uric acid crystals can also be found in joint fluid. Interestingly, uric acid crystals in joint aspirates show negative birefringence and an elongated appearance.
Why is Identifying Urine Crystal Shapes Important?
Knowing the shape of urine crystals can aid in diagnosing the type of kidney stone present, which in turn can guide treatment and preventive measures. For instance, identifying hexagonal cysteine crystals points towards cystinuria, a genetic condition requiring specific management.
Shop related blood tests
Comprehensive Metabolic Panel (CMP)
This panel includes tests for electrolytes (like calcium), kidney function (creatinine, BUN), and uric acid. Abnormal levels of these substances in the blood can contribute to the formation of certain types of urine crystals and kidney stones discussed in the post (calcium oxalate, struvite, uric acid).
Read next
 Written on 02/26/2025
Written on 02/26/2025What Are Common Quadriceps Injuries Like Strains and Contusions, How Do They Happen, What Are the Symptoms, and What Are the Treatment Approaches?
The quadriceps are a powerful group of four muscles located in the front of your thigh. They play a crucial role in extending your knee and, in the case of the rectus femoris, also assist with hip flexion. Unfortunately, these strong muscles are susceptible to injury, particularly during sports and activities involving sprinting, jumping, and sudden changes in direction. Read more
 Written on 01/29/2025
Written on 01/29/2025Phenytoin: How does it work, what are its side effects, and what is fetal hydantoin syndrome?
Phenytoin is a widely used antiepileptic medication, but understanding its mechanism, side effects, and potential risks, like fetal hydantoin syndrome, is crucial. This blog post will break down the key aspects of phenytoin. Read more
 Written on 01/01/2025
Written on 01/01/2025What are the key differences between anti-centromere and anti-scleroderma 70 antibodies in scleroderma, and how do they impact diagnosis and prognosis?
Scleroderma, a complex autoimmune disease, presents diagnostic and prognostic challenges. Understanding the roles of anti-centromere and anti-scleroderma 70 (anti-topoisomerase 1) antibodies is crucial for effective management. This post will delve into their key differences and clinical implications. Read more
 Written on 02/22/2025
Written on 02/22/2025What Is Tinnitus? Causes and Treatment
Tinnitus is a perception of noise or ringing in the ears or head when there is no external source of sound. Read more